SaaS, or Software as a Service, has become a dominant business model due to its scalability and profitability. The SaaS market is expanding rapidly, with thousands of companies worldwide leveraging this model. By late 2024, it’s expected that nearly all businesses will incorporate SaaS products into their operations.
This overview provides insights into 21 different SaaS businesses, highlighting their unique applications and successes. These examples range from established companies with extensive global operations to emerging start-ups making significant impacts. Covering various domains such as project management and customer relationship management, this exploration underscores the broad applicability and transformative potential of SaaS solutions.
What is SaaS?
SaaS, or Software as a Service, is a model where software is provided online through the cloud. Instead of installing and maintaining software on individual computers, users access it via their web browser. This setup allows users to run their business operations, manage projects, or communicate with colleagues from virtually anywhere.
SaaS operates on a subscription-based pricing model, enabling users to pay only for the features and services they use. This model includes several advantages: the SaaS provider manages software updates, maintenance, and data storage in real-time. This approach ensures users can focus on their tasks without worrying about the technical aspects of software management.
While SaaS is a prominent cloud-based model, it’s worth noting that PaaS (Platform as a Service) and IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) are other cloud solutions offering different levels of control and management. For a detailed comparison, you might explore resources that explain how SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS differ.
18 Examples of SaaS Applications with Use Cases
SaaS applications are designed for ease of use and cost-effectiveness, typically requiring just an internet connection. They simplify tasks like onboarding and installation, providing a smooth user experience. Below, you’ll find examples of SaaS platforms making a significant impact in various industries.
Example 1: Asana
Use Case for Asana: Manages tasks and projects with customizable boards and real-time updates, helping teams stay organized and meet deadlines efficiently.
Details:
- Launched: 2011
- Revenue: $652.5 million (2023)
Asana’s features include:
- Flexible task management and project views
- Interactive timeline and calendar features
- Integration with other productivity tools
- Collaborative task assignments and comments
- Real-time progress updates and notifications
Example 2: Salesforce
Use Case for Salesforce: Centralizes customer data to support sales, marketing, and customer support, improving relationship management and business insights through integrated CRM tools.
Details:
- Launched: 1999
- Revenue: $34.8 billion (2023)
Salesforce’s features include:
- Centralized customer relationship management
- Advanced automation for marketing and lead nurturing
- Customizable analytics and reporting
- Integration with numerous business applications
- Comprehensive customer interaction tools
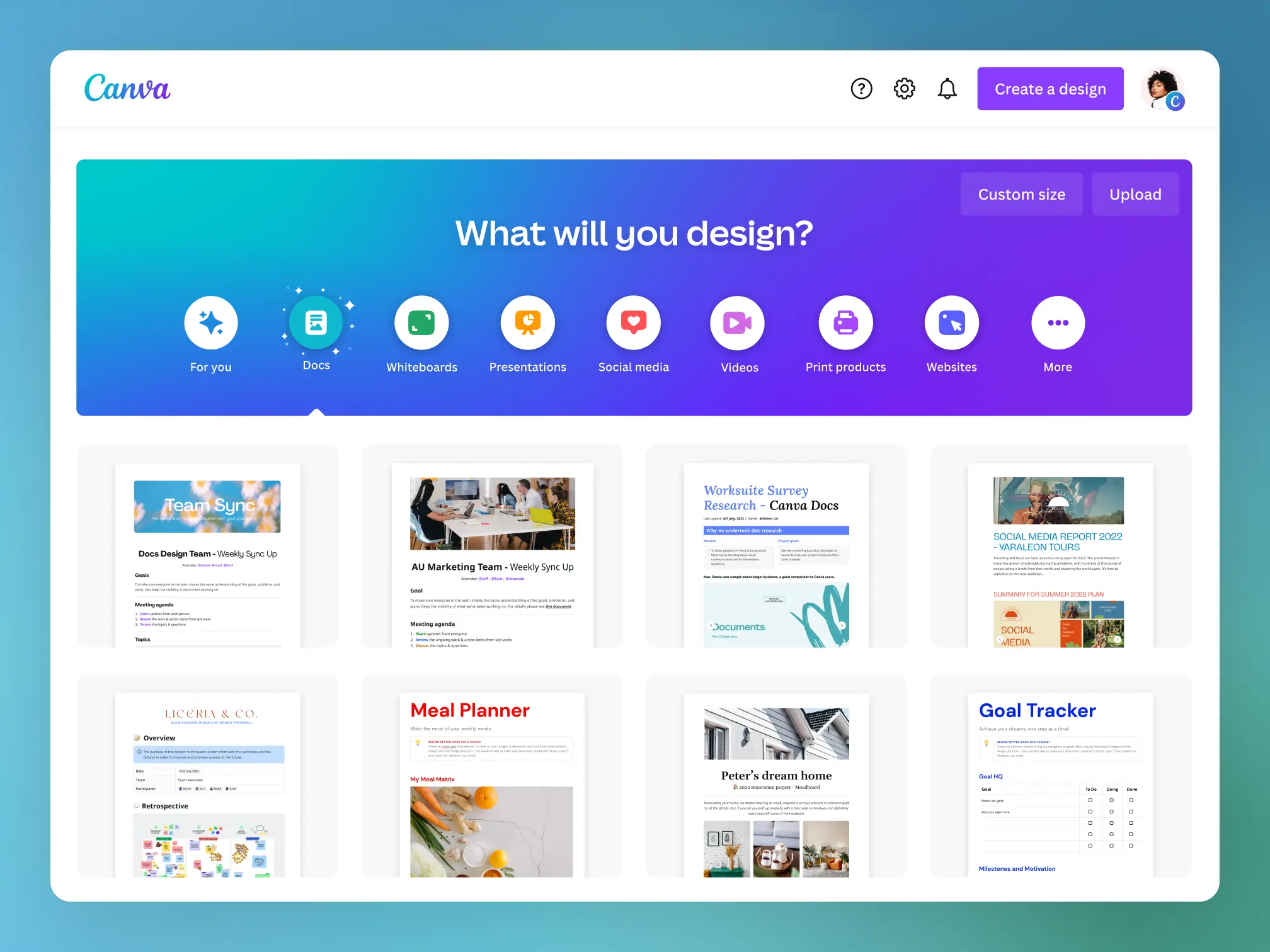
Example 3: Canva
Use Case for Canva: Simplifies graphic design with an easy-to-use platform, offering tools for creating professional-quality visuals and marketing materials.
Details:
- Launched: 2013
- Revenue: $2 billion (2023)
Canva’s features include:
- Extensive library of design templates
- Drag-and-drop design interface
- Custom branding and advanced photo editing tools
- Creation of various graphics and documents
- Collaborative design features
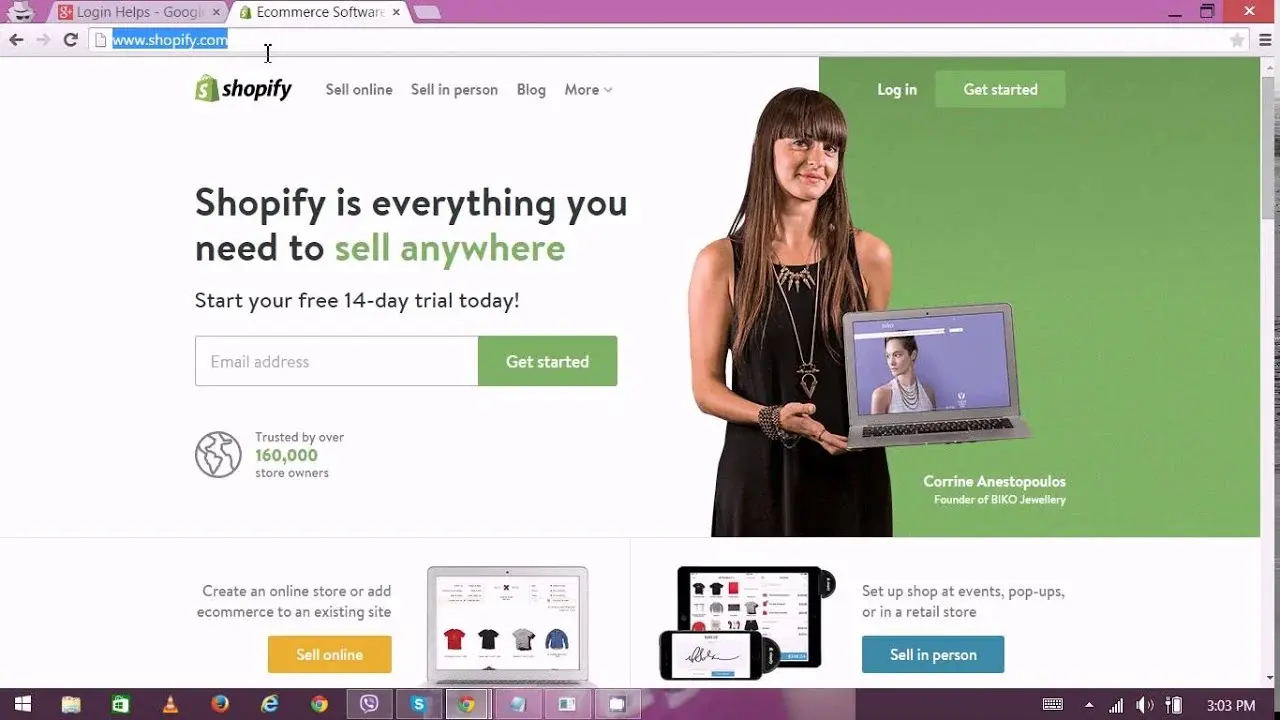
Example 4: Shopify
Use Case for Shopify: Provides an all-in-one e-commerce solution for setting up and managing online stores, including inventory management and payment processing.
Details:
- Launched: 2006
- Revenue: $7.1 billion (2023)
Shopify’s features include:
- E-commerce platform for store management
- Secure payment processing solutions
- Order management and customer support tools
- Customizable store themes and app marketplace
- Analytics and performance tracking
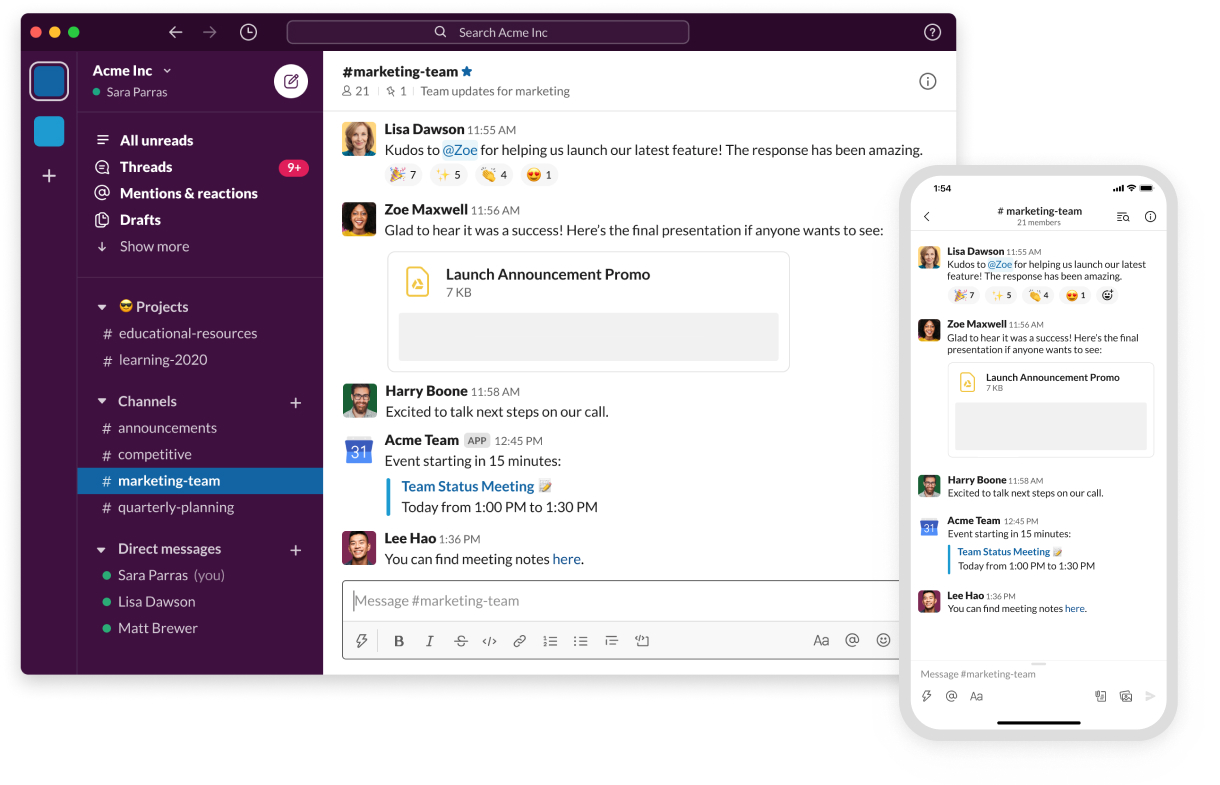
Example 5: Slack
Use Case for Slack: Facilitates team collaboration with real-time messaging, organized channels, and file sharing, reducing email clutter and enhancing communication efficiency.
Details:
- Launched: 2013
- Revenue: $903 million (2020)
Slack’s features include:
- Intuitive mobile and desktop apps
- Robust integration with third-party tools
- Real-time file sharing and collaborative editing
- Customizable notifications and mentions
- Text, voice, and video communication options
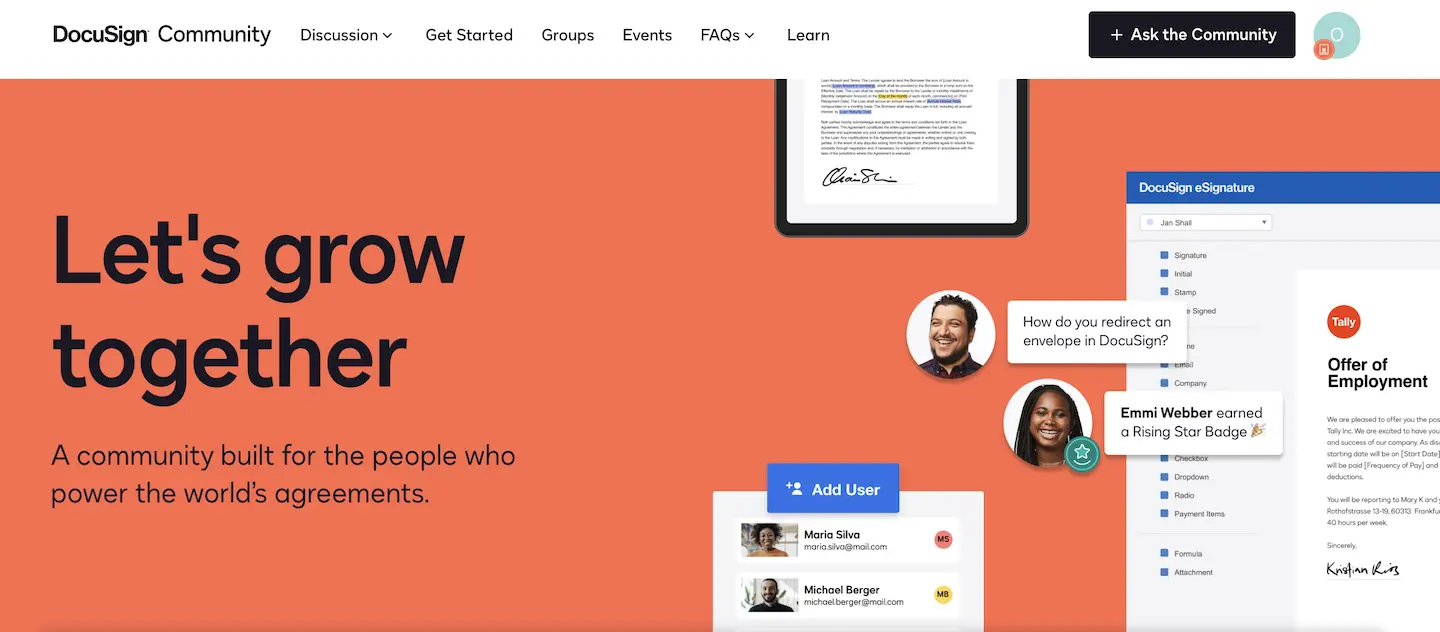
Example 6: DocuSign
Use Case for DocuSign: Allows remote signing of documents, such as contracts and agreements, speeding up transactions with secure, electronic signatures.
Details:
- Launched: 2003
- Revenue: $2.6 billion (2024)
DocuSign’s features include:
- Digital signature capabilities with customizable fields
- Streamlined document merging and PDF conversion
- Pre-designed and adjustable signature templates
- Secure document storage and audit trails
- Options to draw or choose from various signature fonts
Example 7: Trello
Use Case for Trello: Manages tasks and projects using boards, lists, and cards, offering a visual and flexible approach to organizing work and tracking progress.
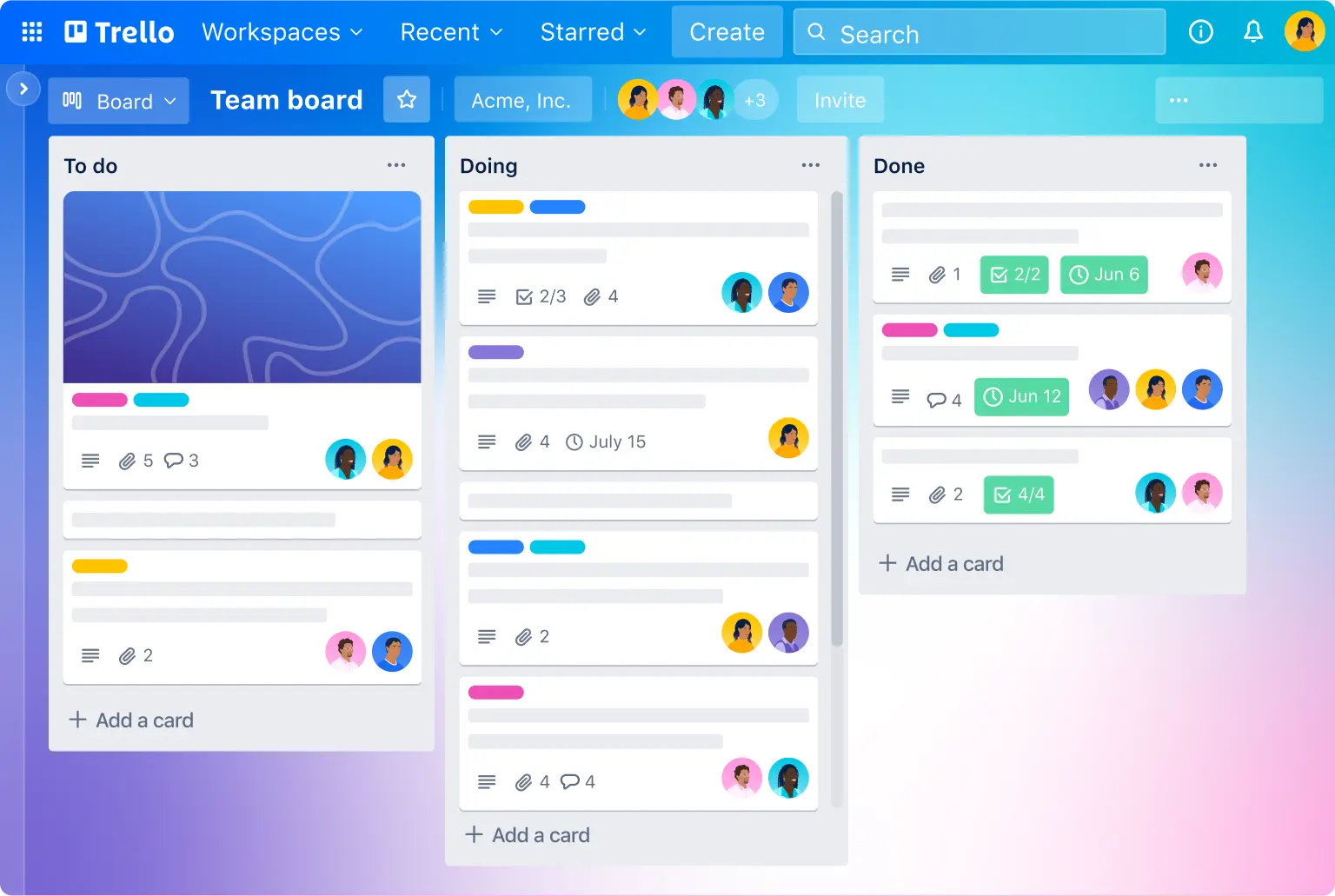
Details:
- Launched: 2011
- Revenue: $425 million (2023)
Trello’s features include:
- Visual boards with customizable lists and cards
- Drag-and-drop task management
- Collaborative features for team projects
- Integration with various tools and apps
- Checklists, labels, and due dates
Example 8: Zoom
Use Case for Zoom: Facilitates virtual meetings and webinars with high-quality video and audio, supporting both personal and professional remote communication needs.
Details:
- Launched: 2013
- Revenue: $4.4 billion (2023)
Zoom’s features include:
- High-definition video and audio conferencing
- Webinar and meeting hosting capabilities
- Screen sharing, virtual backgrounds, and recording
- Real-time transcription and accessibility features
- Integration with scheduling tools
Example 9: Dropbox
Use Case for Dropbox: Facilitates cloud storage and file sharing with synchronization across devices, enabling real-time collaboration and secure file management.
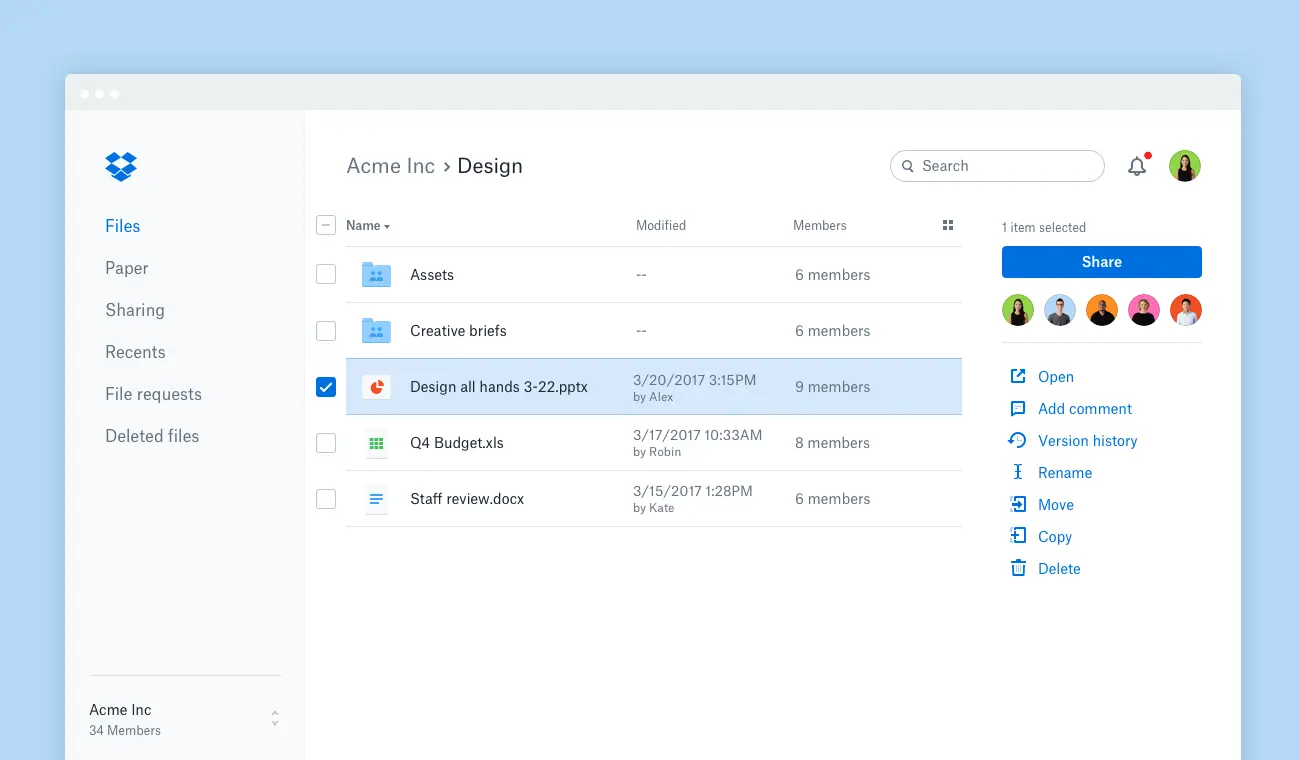
Details:
- Launched: 2008
- Revenue: $2.5 billion (2023)
Dropbox’s features include:
- Seamless device synchronization
- Secure file sharing with permission settings
- Version control for tracking file changes
- Shared folders and collaboration tools
- Integration with various applications
Example 10: Google Workspace
Use Case for Google Workspace: Facilitates collaboration and productivity with integrated tools like Gmail, Google Docs, and Drive, supporting both personal and professional tasks.
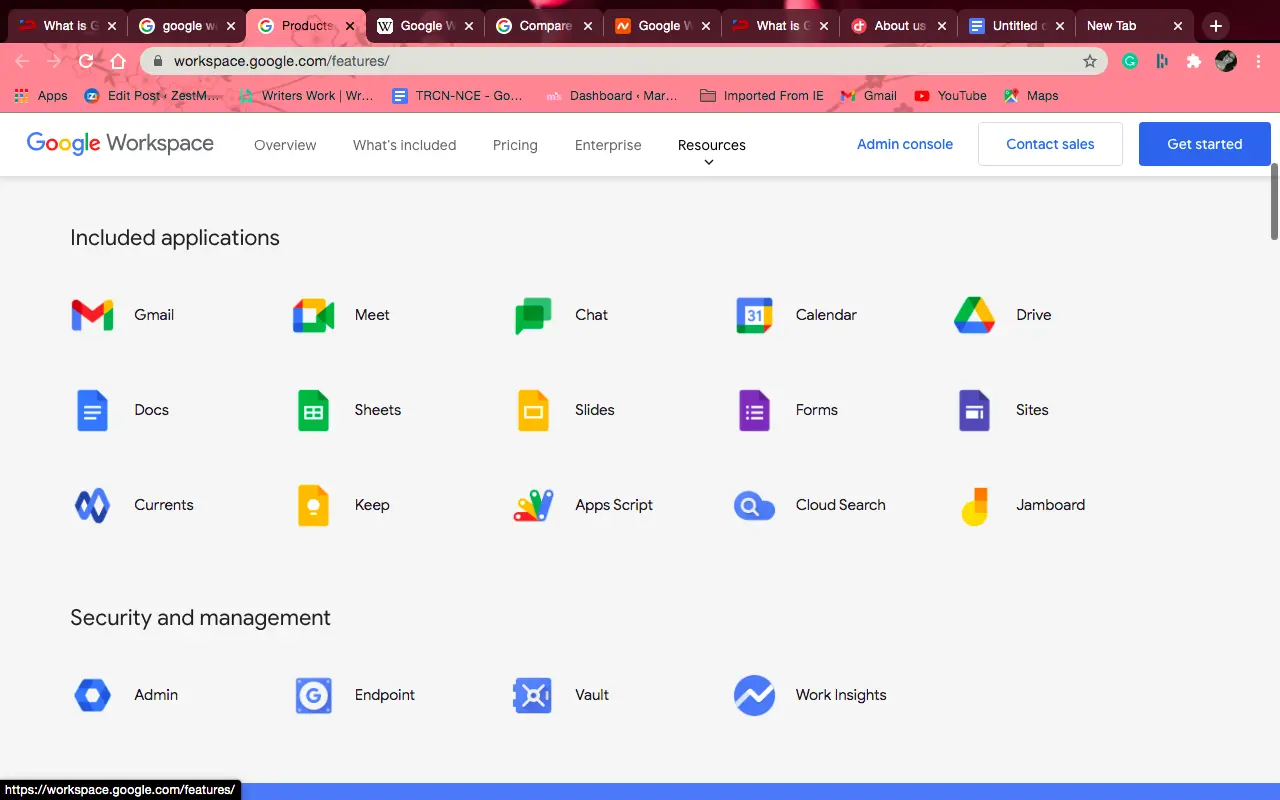
Details:
- Launched: 2006 (as Google Apps, rebranded to Google Workspace in 2020)
- Revenue: $33 billion (lifetime)
Google Workspace’s features include:
- Cloud-based email, document, and collaboration tools
- Real-time collaborative editing and file sharing
- Integrated calendar and task management
- Customizable forms and data collection
- Advanced security and administration options
Example 11: Microsoft Azure
Use Case for Microsoft Azure: Offers cloud computing services for developing, deploying, and managing applications and data, providing scalable and secure solutions for businesses.
Details:
- Launched: 2010
- Revenue: $62 billion (2023)
Microsoft Azure’s features include:
- Comprehensive cloud computing services
- Scalable data storage and management
- Application development and deployment tools
- Advanced cloud-based networking solutions
- Integration with Microsoft and third-party applications
Example 12: QuickBooks
Use Case for QuickBooks: Streamlines financial management with accounting software for small to medium-sized businesses, handling tasks such as invoicing, expense tracking, and financial reporting.
Details:
- Launched: 1983
- Revenue: $5.9 billion (2023)
QuickBooks’s features include:
- Comprehensive accounting and bookkeeping tools
- Invoicing, expense tracking, and payroll management
- Financial reporting and tax preparation
- Integration with banking and payment systems
- Customizable financial dashboards
Example 13: Zendesk
Use Case for Zendesk: Provides a customer service platform for managing support tickets, interactions, and resolutions, enhancing customer support and satisfaction.
Details:
- Launched: 2007
- Revenue: $1.3 billion (2023)
Zendesk’s features include:
- Support ticket management and automation
- Multi-channel customer interaction tools
- Customizable knowledge base and help center
- Analytics and reporting for support metrics
- Integration with various CRM and business tools
Example 14: Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Use Case for AWS: Provides a comprehensive suite of cloud services, including computing power, storage, and databases, supporting scalable and flexible cloud solutions for businesses.
Details:
- Launched: 2006
- Revenue: $87.8 billion (2023)
AWS’s features include:
- Broad range of cloud computing services
- Scalable storage and data management
- Robust infrastructure for application hosting
- Advanced analytics and machine learning tools
- Security and compliance features
Example 15: Freshdesk
Use Case for Freshdesk: Manages customer support through a ticketing system, knowledge base, and automation, streamlining customer service processes and improving response times.
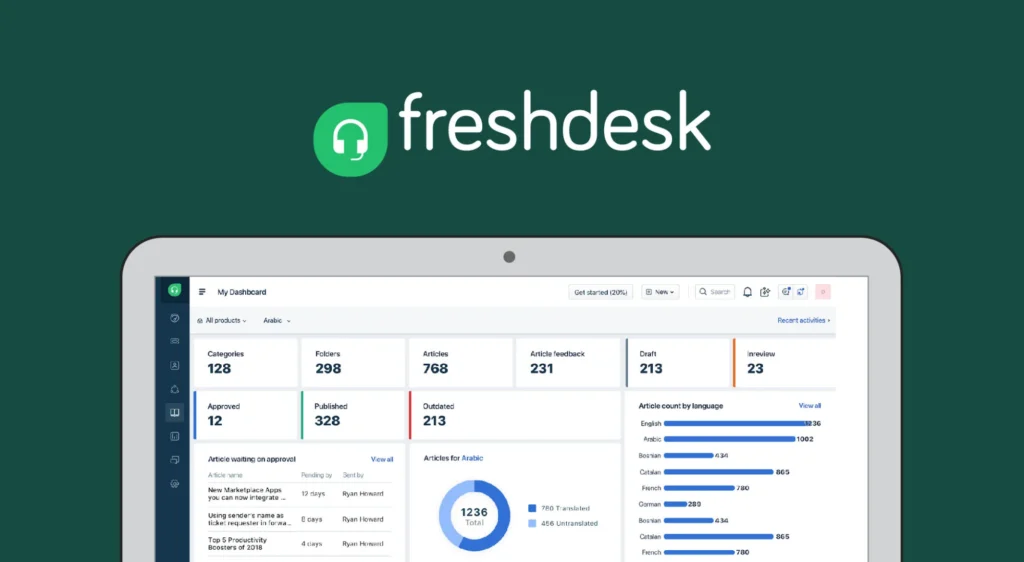
Details:
- Launched: 2010
- Revenue: $425 million (2023)
Freshdesk’s features include:
- Ticket management and automation
- Multi-channel support (email, chat, phone)
- Knowledge base and self-service options
- Customer feedback and satisfaction tracking
- Integration with CRM and other tools
Example 16: Box
Use Case for Box: Offers cloud storage and collaboration tools for managing files and workflows, providing secure access and sharing options for teams.
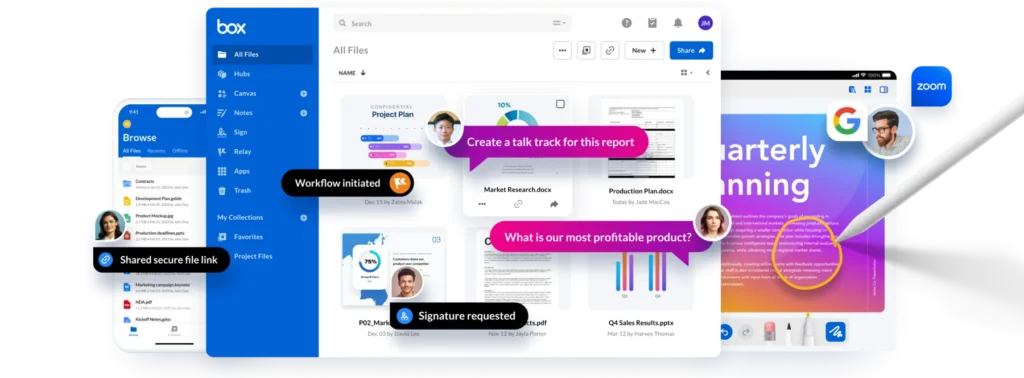
Details:
- Launched: 2005
- Revenue: $947 million (2023)
Box’s features include:
- Secure cloud storage with file sharing capabilities
- Collaborative tools for document editing and comments
- Integration with various productivity apps
- Version history and access controls
- Advanced security and compliance features
Example 17: Netflix
Use Case for Netflix: Provides on-demand access to a vast library of movies and TV shows, including exclusive original content, with personalized recommendations and offline viewing options.
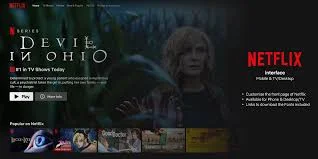
Details:
- Launched: 1997 (streaming in 2007)
- Revenue: $39.2 billion (2023)
Netflix’s features include:
- Extensive library of on-demand content
- Personalized recommendations based on viewing history
- Offline viewing with downloadable content
- Exclusive original series and movies
- Multi-device streaming support
Example 18: Basecamp
Use Case for Basecamp: Provides project management and team collaboration tools, offering features like task management, scheduling, and real-time communication.
Details:
- Launched: 2004
- Revenue: $75 million (2023)
Basecamp’s features include:
- Project and task management tools
- Real-time team communication and collaboration
- Shared schedules and document storage
- To-do lists and milestones
- Integrated messaging and file sharing
Ready to Build Your Own SaaS Success Story?
At Unoiatech, we specialize in helping businesses bring their SaaS vision to life. Whether you’re looking to scale, optimize, or launch from scratch, our team has the expertise to make it happen. Want to see how we helped one of our clients build a $900M SaaS product? Check out our case study here and discover how we can do the same for you.