What is Artificial Intelligence (AI) Automation, and How Do We Implement It?.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) automation is the use of AI to enhance business operations by mimicking human intelligence. AI automation processes data at high speed, improving efficiency, reducing costs, and optimizing workflows. By implementing AI automation, companies can streamline tasks through evolving technologies like machine learning (ML) and natural language processing (NLP).
A McKinsey Global Survey revealed that 65% of respondents reported using generative AI in their operations, almost double from the previous year.
Automation can fuel growth, reduce costs, boost productivity, and enhance customer retention, but it needs to be applied strategically, aligning with specific business objectives. AI adds real value when it’s used to complement sound methodologies and well-defined processes.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI) Automation?
AI automation in business falls into three categories:
- Assisted Intelligence: This involves automating straightforward or repetitive tasks.
- Augmented Intelligence: This type learns from human actions over time to enhance overall performance.
- Automated Intelligence: Here, decisions are made entirely by machines without human intervention.

Implementing any of these AI types helps meet automation goals, aiming to enhance departmental performance and achieve key performance indicators (KPIs), rather than merely replacing human efforts.
AI-driven automation generally combines Business Process Management (BPM), Robotic Process Automation (RPA), and AI itself. BPM automates workflows and integrates systems, RPA uses bots for repetitive tasks, and AI leverages data to make predictive decisions. Together, these components form a robust automation framework.
While RPA bots follow predefined rules, AI extends capabilities by learning and refining responses over time, making it a valuable tool for process mining within BPM, offering deep insights through advanced analytics.
Is AI the Same as Automation?
AI and automation are interrelated but distinct concepts. AI acts as an enabler, enhancing automation by adding speed, accuracy, and consistency where needed. Think of automation as the vehicle speeding up your processes, while AI is the onboard system optimizing the route, diagnosing issues, and providing maintenance advice.
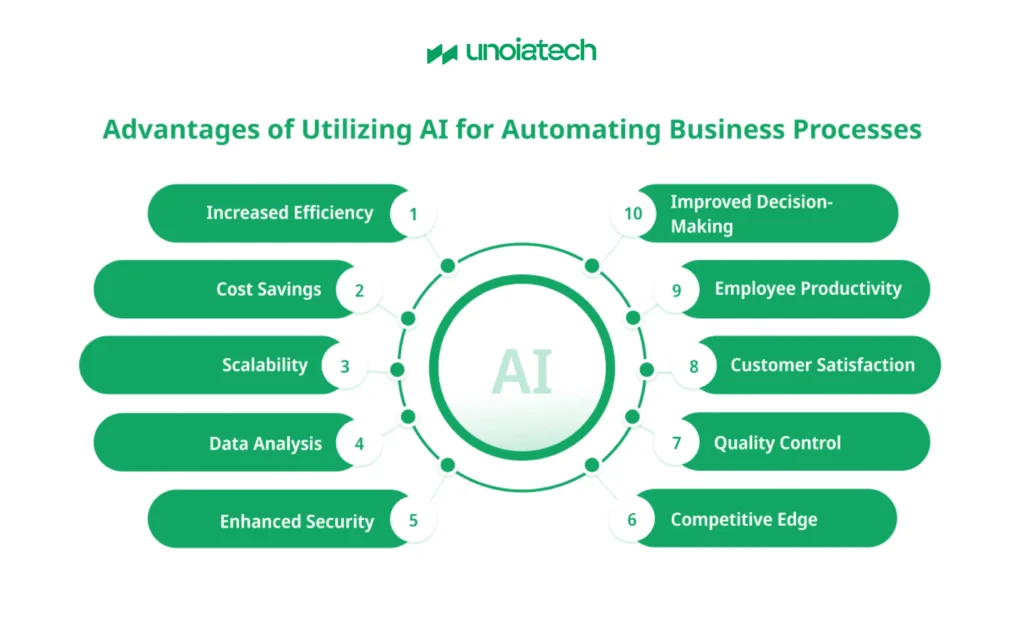
Benefits of Automating Business Processes with AI
Integrating AI automation offers several advantages, including:
- Improved Customer Service: With AI automation, chatbots handle basic queries 24/7.
- Cost Savings: AI automation reduces human error and streamlines workflows, cutting operational costs.
- Faster Decision-Making: AI automation speeds up decision-making processes through data analysis.
According to PwC, AI could increase global GDP by up to 14% within the next six years, contributing an estimated $15.7 trillion by 2030 through enhanced productivity and consumption. AI frees human employees to focus on more complex tasks such as strategy, engagement, and innovation, while integrating with automation to transform business operations.
 Improved Customer Service: AI enhances customer service with 24/7 availability, handling high volumes of tickets and reducing wait times. AI-driven chatbots manage basic inquiries and resolve issues, escalating only when necessary. Real-time language detection and translation tools facilitate global support, while AI’s conversational capabilities create an intuitive user experience.
Improved Customer Service: AI enhances customer service with 24/7 availability, handling high volumes of tickets and reducing wait times. AI-driven chatbots manage basic inquiries and resolve issues, escalating only when necessary. Real-time language detection and translation tools facilitate global support, while AI’s conversational capabilities create an intuitive user experience.- Legacy Data Reclamation: AI’s intelligent document processing (IDP) retrieves data from unstructured sources like ledgers and invoices, while image scanning adds extra inputs, reclaiming valuable data from legacy systems.
- Cost Savings: AI reduces operational costs by improving accuracy, resource management, and reducing repetitive work. It minimizes waste through quality control, operates 24/7, and automates data entry, troubleshooting, and management tasks, all of which contribute to cost reduction.
- Faster Decision-Making: AI accelerates decision-making through simulations, trend forecasting, and prescriptive analytics, processing large datasets quickly and offering targeted recommendations. It enables agile responses and faster, data-informed decisions, though complex decisions still benefit from human oversight.
- Better Process Efficiency and Excellence: AI excels in process discovery by identifying patterns and mapping out complex systems. It enhances time management, output consistency, and overall performance by automating repetitive, rule-based tasks that require minimal human input.
- Process Standardization: AI aids in standardizing procedures, tracking KPIs, and reducing redundancies. It creates visual aids like flowcharts and infographics, optimizing workflows based on actual metrics to produce consistent results and reduce impromptu workarounds.
Challenges of Adopting AI Automation and How to Overcome Them
AI and automation can’t fix broken processes on their own. Success depends on having stable workflows in place before automation begins. AI can flag which processes need standardization before being automated.
Cultural resistance to change is common, especially in organizations tied to legacy systems. Empowering employees to actively engage with new tools will ease friction and ensure successful implementation. Executives also need a clear understanding of long-term automation goals to maintain their support.
A lack of vision leads to wasted investment and stalled initiatives. It’s crucial to identify the right technologies and understand their applications before committing. Take a holistic view of processes and data flows to determine where AI can offer the most value.
Every automation project incurs costs. Before diving into AI, businesses must weigh the initial investment against long-term savings, factoring in tech costs, talent acquisition, and potential ROI.
According to a 2024 MIT study, only 23% of worker tasks can be automated without added costs. Automation is a continuous process that requires ongoing validation and refinement. AI must be regularly assessed to ensure it’s contributing effectively.
Digital transformation is most successful when AI is integrated as a tool to support existing systems, not a standalone solution. Building transparency, assessing risk, and acquiring the right talent are all essential to ensuring AI-driven automation delivers sustainable improvements.
Data Privacy
AI models, especially foundational ones, are pre-trained on vast datasets, often sourced from public data or web scraping. These deep learning models adapt to various tasks but raise concerns about bias, inaccuracy, and potential exposure to toxic content. Additionally, some of the data used may violate copyright, license, or intellectual property laws.
Companies must safeguard customer trust by vigilantly managing data privacy, ensuring that sensitive information is not misused or collected beyond its intended scope. With the rise of IoT-generated data, the challenge of protecting customer privacy and data security grows more urgent.
Labor Market Impacts
AI’s rapid adoption is already reshaping industries like healthcare, finance, automotive, logistics, retail, and manufacturing. This shift is creating new opportunities for skilled workers, particularly data scientists and engineers, while reducing the demand for roles like data entry or call center staff.
To stay competitive, businesses should prioritize roles that AI can’t easily replace—such as those requiring leadership, creativity, ethics, and supervision. Strategic hiring will focus on areas where humans can complement automated processes, ensuring long-term relevance in an AI-driven world.
Employee Acceptance and Training
The future workforce will combine AI and human workers, working together toward business goals. Employees should view AI training as a chance to enhance their skills and collaborate in problem-solving. Low-code/no-code development makes it easier for employees to reskill and participate in workflow automation, democratizing the process and encouraging cross-functional innovation.
AI tools have a lower learning curve than traditional technologies, making them accessible to a broader range of users and promoting a more inclusive approach to development.
AI Automation Examples
AI automation is transforming industries by following human-defined rules and generating predictive solutions. In sectors like manufacturing and freight, AI-driven bots are streamlining supply chains, forecasting inventory needs, and flagging potential disruptions, such as weather-related delays.
The banking industry increasingly uses AI to assist customers, monitor transactions, and detect fraud. AI supports investment planning, shaping customer experiences, and building stronger predictive models for better risk management. Similarly, the insurance sector has embraced AI for claims processing, underwriting, and compliance.
Retail has been revolutionized by AI, with personalized shopping experiences, improved recommendation engines, and customer segmentation based on purchasing behavior. AI not only enhances productivity but also elevates customer expectations by providing tailored solutions and more predictive, data-driven shopping experiences.
IT
AI automation in IT empowers users to manage their workflows independently, allowing IT teams to focus on strategic priorities like security and stability. With AI managing day-to-day problem-solving tasks, IT departments can shift their attention to larger issues.
AI also streamlines cloud services, speeding up updates and reducing the need for on-premises hardware, freeing up physical space. This is especially beneficial for data-heavy needs like media archiving. IT teams may also rely on AI for managing data integrity, computing power, and system parameters, ensuring a smooth digital transformation.
Procurement
AI helps procurement teams by refining spend management processes. Through audits, AI can assist in analyzing requisitions, managing contracts, and flagging potential issues. It also helps predict spending trends and respond to changing market conditions.
Sourcing is simplified with AI, as it handles repetitive tasks, such as filling out forms and collating vendor data, all while offering data-driven recommendations. In the future, AI’s scalability may shift its focus from firm-specific applications to industry-wide uses, especially benefitting smaller businesses with limited resources.
HR
AI is transforming HR departments by automating manual and repetitive tasks, such as data entry. For hiring, AI can screen resumes, schedule interviews, and match candidates to job requirements. It also enhances employee onboarding and engagement by standardizing processes. Performance reviews, attendance tracking, and document classification can be streamlined with AI, freeing HR staff to focus on more strategic tasks.
How to Start Using AI Automation at Your Company
Strategic planning is crucial for introducing AI automation into your business. Start small, automating one process at a time to avoid overwhelming data silos. Use process discovery and mining to understand both human and data behaviors. Solicit employee feedback and define desired outcomes before making technology investments.
AI requires continuous human oversight, especially in regulated industries. Tracking AI performance over time with regular audits and KPIs helps align automation with business goals. Here are key steps for successful AI automation:
- Define your goals with stakeholder input
- Establish use cases and identify historical data value
- Prioritize processes for automation
- Assess potential security risks
- Choose the right technology
- Hire or upskill team members
- Plan training and implementation
- Start with a pilot program and scale gradually
- Continuously monitor results and test for validity
- Implement governance policies to oversee AI initiatives



 Improved Customer Service: AI enhances customer service with 24/7 availability, handling high volumes of tickets and reducing wait times. AI-driven chatbots manage basic inquiries and resolve issues, escalating only when necessary. Real-time language detection and translation tools facilitate global support, while AI’s conversational capabilities create an intuitive user experience.
Improved Customer Service: AI enhances customer service with 24/7 availability, handling high volumes of tickets and reducing wait times. AI-driven chatbots manage basic inquiries and resolve issues, escalating only when necessary. Real-time language detection and translation tools facilitate global support, while AI’s conversational capabilities create an intuitive user experience.