What is Workflow Automation?
Workflow Automation is a transformative approach that leverages software to handle tasks and activities which would otherwise require human effort. By implementing workflow automation, businesses can streamline their processes, increase efficiency, and reduce the reliance on manual input. This guide will delve into the benefits of workflow automation, provide examples, and offer a step-by-step approach to implementing it effectively.
Workflow Automation Examples
Now that you understand what workflow automation is, let’s dive into a few examples. Nearly every workflow includes tasks that can be automated to some degree. However, the extent of automation will vary depending on the nature of the workflow. Here are some commonly automated tasks:
- Emails and form submissions are converted into service requests.
- Calendar events and meeting invites are automatically created and sent.
- Workloads are distributed based on volume, time, or other criteria.
- Tasks are routed or assigned to the correct team member.
- Automated emails or notifications are triggered when task statuses change.
- Alerts are generated when deadlines are near or a task is overdue.
- Messages are sent via communication platforms like Slack, WhatsApp, or SMS.
- Documents and contracts are auto-generated and sent for e-signature.
- Notifications are sent out when approvals or reviews are required.
- Data is automatically synced when an email is received or a form is filled out.
- Reports and dashboards are generated from workflow data.
There are many opportunities to automate repetitive and predictable tasks in most workflows. Generally, if a task is simple, scheduled, or frequently occurring, it’s a good candidate for automation. When multiple tasks are automated, the entire workflow becomes more efficient.
By integrating a workflow management system with other applications, even more complex automation can be achieved.
Key Advantages of Automated Workflows
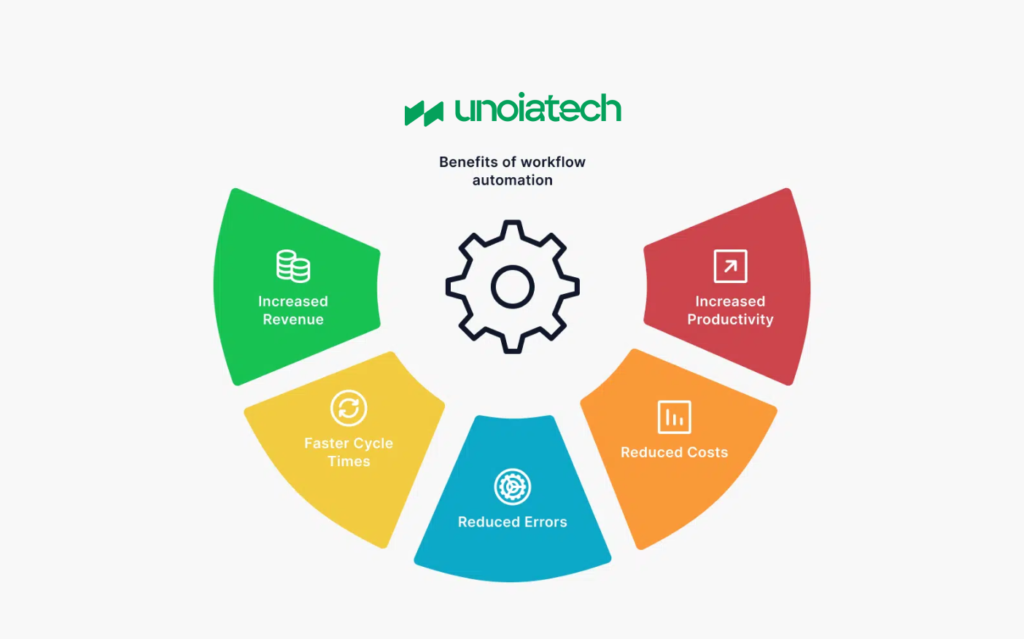
- Higher Productivity: Automation reduces repetitive tasks, allowing employees to focus on strategic, high-value work.
- Cost Savings: Streamlined workflows save money by requiring less time, effort, and resources.
- Efficiency: Automating routine processes reduces wasted time and enhances the overall flow of work.
- Collaboration: Automation improves team collaboration by providing access to work items across departments.
- Accuracy: Reduces errors by minimizing manual inputs and keeping records updated in real-time.
- Speed: Tasks progress faster without manual intervention, expediting workflow completion.
- Communication: Automated notifications, emails, and alerts help keep everyone informed, reducing communication gaps.
- Accountability: Tasks can be assigned to specific individuals, clarifying responsibility for each step.
- Visibility: Managers gain insights into workflow progress, aiding in tracking tasks and meeting deadlines.
- Employee Experience: Automation prevents burnout by eliminating repetitive tasks, allowing employees to focus on engaging work.
How to Automate Workflows: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Define the Workflow: Clearly outline the start, end, and output of the workflow to understand its purpose and scope.
- Identify All Actors: Determine who is involved in each step, including those responsible for reviewing or passing along tasks.
- List Systems, Apps, and Tools: Identify all systems, apps, and tools—such as ERPs, CRMs, and collaboration platforms—that play a role in the workflow.
- Note Input Avenues: Record all sources of input, including emails, forms, and data from other systems that feed into the workflow.
- Track Handoffs: Pinpoint where tasks change hands, as these transitions are often sources of delays or confusion.
- Create an Automation Wishlist: List the tasks that could benefit from automation based on your workflow analysis.
- Build the “To-Be” Workflow: Use automation tools to create a new, optimized version of your workflow, incorporating automation.
- Test the Workflow: Run a test to ensure that the new workflow functions as expected and that no bottlenecks or issues arise.
- Train Your Users: Ensure your team understands how to use the new system and is comfortable with the updated workflow.
- Deploy, Monitor, and Optimize: Launch the workflow, then monitor it regularly to identify areas for further improvement.
Workflow Automation vs. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
The rise of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) has led many teams to evaluate whether they need workflow automation or RPA. In many cases, businesses benefit from both. Each technology offers distinct advantages depending on the specific use case.
- Workflow Automation: Focuses on defining processes by outlining triggers, tasks, inputs, and results. It automates tasks, communications, and status updates using low-code tools that allow business users to design and manage workflows through a visual interface.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Utilizes code-based bots to handle individual tasks. These bots require manual coding and reprogramming for task changes. While bots can be linked for complex processes, modifications often necessitate updates to multiple tasks.
Organizations often employ both workflow automation and RPA as part of a comprehensive business process management strategy, leveraging each where it fits best.
What is workflow automation software?
Workflow automation software, also known as workflow management systems or simply workflow systems, is designed to automate and streamline business processes. Regardless of the name, the key is to choose a platform that offers robust features and integration capabilities. These tools enhance the scope of automations, making work more efficient and effective.
| Spreadsheets | Workflows |
|---|---|
| Troubleshooting or updating broken formulas in spreadsheets is notoriously challenging. | Workflow management tools offer a simple drag-and-drop visual interface, making it easy to create and update automations. With low-code platforms, anyone can make changes without relying on IT. |
| As companies grow, spreadsheets become cumbersome and harder to manage. | Workflow management systems scale smoothly, allowing users to modify and expand automations with ease. Low-code tools empower teams to implement changes quickly. |
| Spreadsheets lack robust controls, making them prone to fraud and difficult to maintain for compliance. | Workflow software includes built-in security and compliance features, reducing the risk of fraud and the effort needed for regulatory adherence. |
What to Look for in Workflow Automation Software
When choosing workflow automation software, consider features that add value and enable seamless integrations. Essential elements include:
Low-Code: Minimizes reliance on IT by allowing business users to automate processes through a visual interface. This feature accelerates workflow optimization and reduces IT burden.
Forms and Portals: Customizable forms simplify data collection, standardize entries, and prevent errors. Portals facilitate secure sharing of forms with internal and external users.
Integrations
Teams often use various systems like ERPs, CRMs, and HRIS to manage their operations. Workflow automation tools should integrate smoothly with these systems to eliminate silos and enhance collaboration. Common integrations include:
- Collaboration Tools: Slack, Zoom, Google Drive, Outlook
- Sales & Marketing: Salesforce, Mailchimp, Marketo, Shopify
- HR Tools: Workday, Zenefits, Docusign, ADP
- Finance Tools: Quickbooks, SAP, Oracle, Sage Intacct
- Social Media: Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter
Templates: Use templates to build workflows quickly. They can be customized to fit unique processes, offering a scalable way to implement and optimize workflows.
Rules and Conditional Logic: Enhance workflow customization with rules and conditional logic, automating routing, field requirements, and notifications to streamline processes.