Usability Testing or User Experience (UX) testing is a method used to evaluate the user-friendliness of a software system such as a website or an app. During the test, selected users are required to complete certain tasks while observers take note of their behaviour and approach followed to complete the task.
Such a test lets us actually see what users do when they visit a website and with how much ease they are able to carry out a specific task. It helps us in identifying the usability problems the users might face, collect data, make decisions and fix the identified problems. A typical test can last from 1 hour to 11/2 hours.
According to Jeff Bezos, CEO of Amazon, investing heavily in the usability design over marketing during Amazon’s first year was the strategy that led to its overwhelming success. IBM reports that every dollar invested in usability brings a return from 10 to 100 dollars.
Why Usability Testing is Important?
Usability tests are an important part of the design process because they determine how well the product works. Usability testing determines whether an application is usable, accessible and useful. These tests help us understand whether the website meets the users’ expectations or not by helping us understand user behaviour. If a user is lost while looking for something on a website, that screams of bad design. A user shouldn’t have to think hard to decide which link to click or which page to navigate next.
How Many Users Are Required?
With the target audience determined, Nielsen Norman Group recommends keeping testing limited to 5 participants. Such a small number of users are enough to uncover nearly 80% of the usability problems. It’s a good idea to choose users who have sufficiently different behavior and varying levels of experience with the product. With User Insights, Playbook UX, etc. you can pay to have people test your website. You can go the DIY route and choose your own testers and save money.
Test Objectives
You have a product, say a music streaming and download website that you want to test and check the user experience. The primary test objective is to determine whether the users (new and existing) can perform a basic function or not, say searching for a music artist or playing a music track. The secondary test objective is to determine with what ease the users are able to perform the task, what they think about the user interface, will they come back to the website and/or recommend it to others.
Methods
A usability study can be conducted using the following methods:
Moderated In-Person
The test is carried out in a lab with moderators to ensure the users go through the test without any help from outside. The moderator watches users interact with the software, perform the task and take notes of their behavior.
Moderated Remotely
This is similar to in-person testing only conducted remotely. A moderator is not physically present with the participants but gets to watch the users interact with the software remotely using screen sharing software.
Unmoderated Remotely
Under this testing method, participants perform the assigned tasks remotely. Their voice, facial expressions, eye movements are recorded with usability software tools. The data is later analyzed by the observers. User Insights, Playbook UX and Userlytics are some of fully-featured usability testing tools used for unmoderated remote testing.
Analyzing Results

Both quantitative and qualitative data can be collected from a usability test.
Quantitative data includes parameters like time taken to complete a particular task, success rate, etc. Qualitative data is gathered from demographic data (age, gender, income, device, location, etc.), and pre-test, post-task and post-test questionnaires.
Say all 5 participants completed Task 1 (search for a music artist) and Task 2 (play a music track), 4 of them completed Task 3 (look for a particular music album) and only 2 of them were able to complete Task 4 (purchase a track). None of them was able to find and use the bulk download feature for downloading multiple tracks.
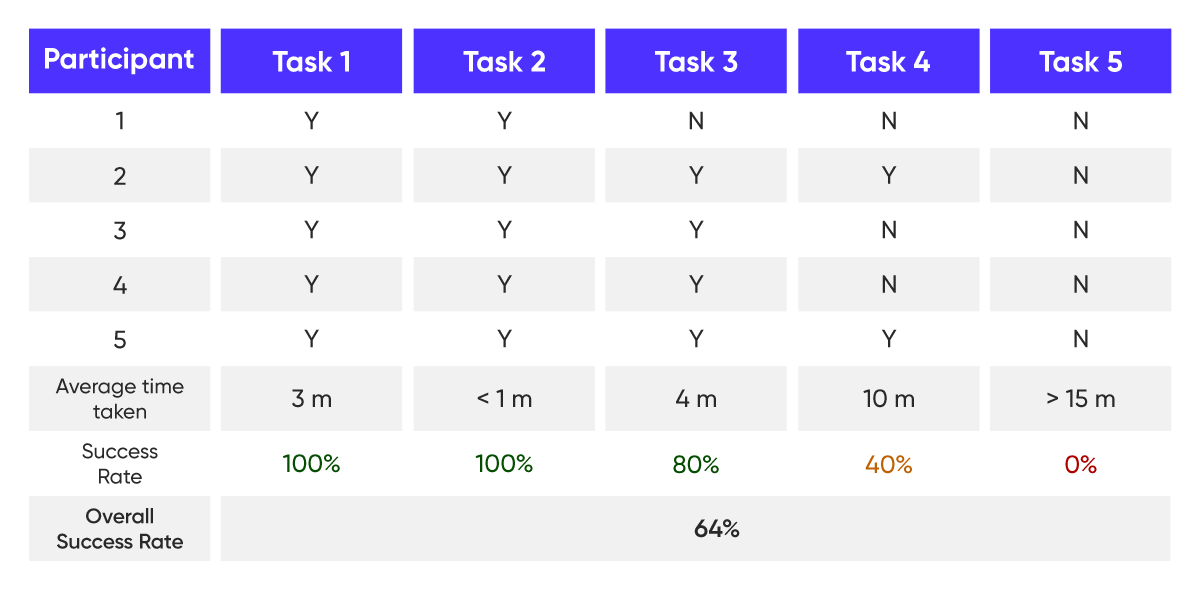
3 participants had trouble completing Task 4 which shows the purchase/payment function can be simplified. None of the users was able to use the bulk download feature which means the function can be displayed more prominently.
A post-task questionnaire helps in gathering qualitative data. An example is shown below:
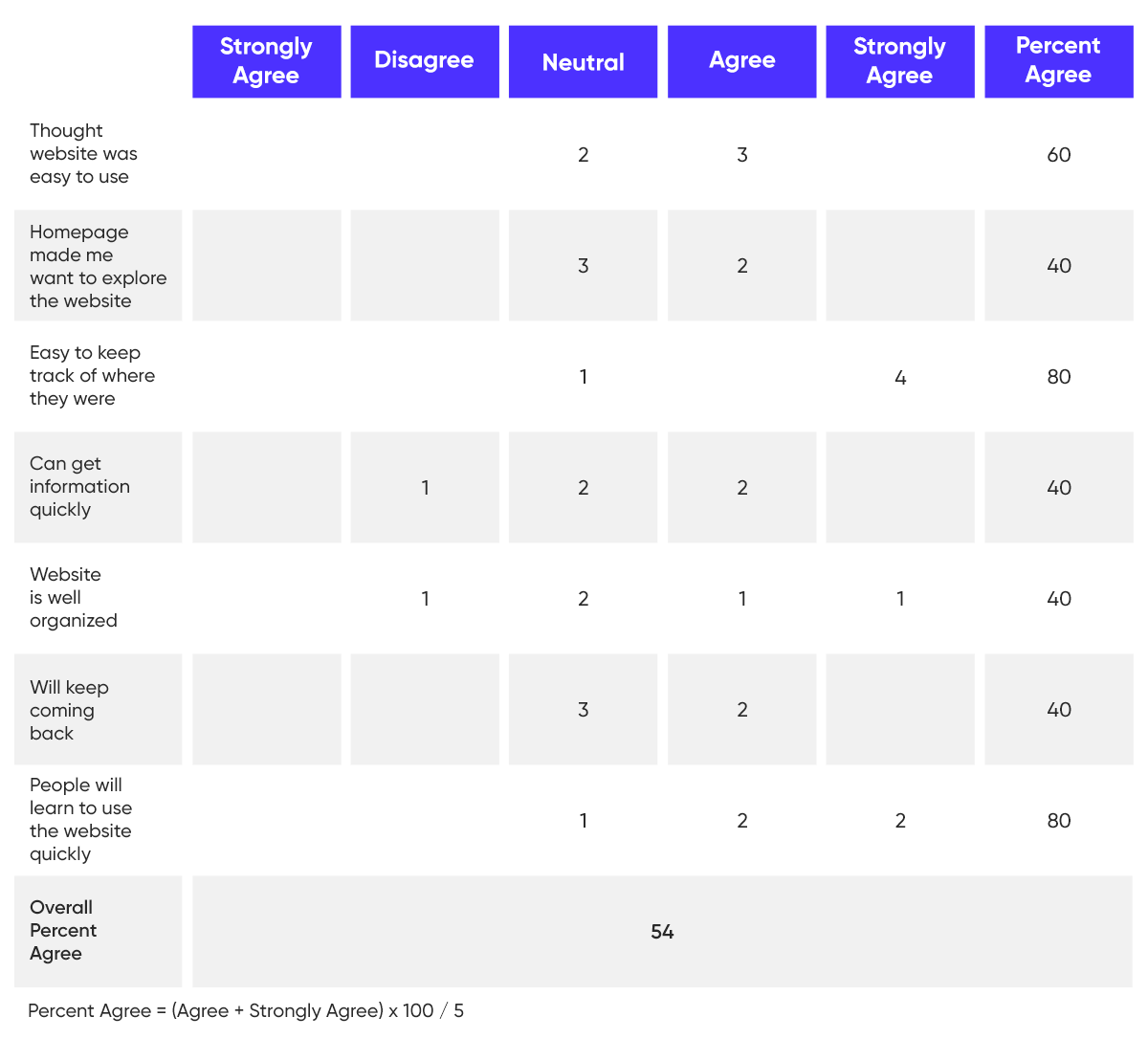
The data shows half of the users were satisfied with the overall website experience. The website doesn’t have a steep learning curve to it which is a good thing. Improvements are needed in the way the information is organized on the website and the way it’s presented to users.
Conclusion
Usability testing helps us learn about the usage patterns and discover the components of the product that work and that don’t. Working with users and addressing the recommendations eventually helps in creating a user-centric product that drives better revenue.